Inverter Terminology: What does is all mean?




An inverter is a device that allows you to run 230v AC appliances from your DC batteries. They are an essential part of an off-grid home and they can make your van or boat feel more like home allowing you to run kettles, microwaves, hairdryers and anything else you would use in a house.
There is a lot of specific terminology surrounding inverters, if you are new to them it's quite easy to be left confused by it all so, so what does it all mean?
By the time you leave this article, you will be an expert when it comes to the different terminology you will see when looking at inverters so you can make an informed purchase. You may also want to read our other article about how to pick the right size of inverter.
Terms we will discuss
Quasi (modified) Sine Wave & Pure (true) Sine Wave
It first helps to understand what a sine wave has to do with inverters, If we go back to basics, in Alternating Current (AC) which comes from your mains plugs, the current flows back and forth (alternating). The sine wave is a visual representation of this flow back and forth of the elections, as an inverter creates a mains supply it has to recreate this for appliances to work, hence the Sine Wave. As you can see below mains output has a smooth transition from ‘forwards’ to ‘backwards’.
Difference between Quasi Sine Wave and Pure Sine wave Inverters
A pure sinewave is near perfect match to the sine wave of a mains supply, A Quasi sinewave also known as a modified sinewave doesn’t recreate this as well and instead of being a smooth change, it changes abruptly. As you can see in the image below the wave produced by a modified inverter has lots of straight lines instead of a smooth curve.
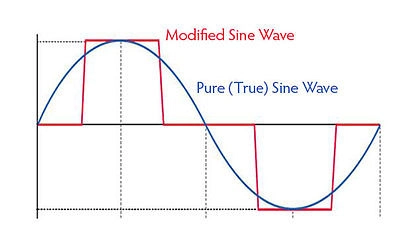
What this really means is Quasi Sine Wave inverters are cheaper than their Pure Sine Wave counterparts. They also can’t be used to power some types of equipment such as fridges, microwaves, compressors, power tools or anything that has an AC Motor, it puts more strain on them which can put more strain on components wearing out your devices quicker. TV’s also don’t work well as lines can appear on the screen.
Less sensitive equipment such as kettles and microwaves work fine with a Modified Sine Wave inverter however as they are designed for a Pure Sine Wave, Quasi-inverters can cause them to run less efficiently, using more of your battery power and can cause those devices to wear out quicker than a Pure Sine Wave would.
Modified sine wave inverters offer a cheaper alternative which is noticeable when you get to the higher-powered inverters which are a fraction of the price. For some people they are fine but pure sine wave inverters have been coming down in price in recent years & with their benefits they are often the go-to option.
What Does VA Rating Mean
You may see some inverters listed with Watts in their title and others that say VA. VA means Volt-ampere which is essentially the potential power, you need to be careful of this as this is not what your inverter will produce, it will often be lower. Make sure to check the specs to see what the actual wattage output is.
Some brands use this value as it is a larger number and it makes their inverters seem more powerful than they actually are.
Continuous Power
Continuous power is the maximum amount of power that the inverter can output for an indefinite number of hours or continuously. This is also what the inverter will be rated at when you see it’s power in the title. Your inverter pulls power as it needs so it won't output this all the time, only if you need it. For example, if your continuous power is rated at 1500w and you have a microwave at 800w it will supply 800w.
Peak Power
Peak power is the amount of power that an inverter can produce for a very short period of time, depending on your inverter it can sometimes be double the continuous rating. This is to be able to handle surge currents.
Some types of appliances (usually ones that include an AC motor) such as fridges, air conditioners or power tools have a surge current when they start up. This is a high inrush of current that only lasts for a fraction of a second but it is much higher than the rated wattage of the device, it can also known as inrush current.
If you plan to run any of the above devices or something else that includes a motor you need to make sure the peak power of the inverter is higher than the surge current to avoid tripping the inverter and causing it to shut off.
Efficiency
Very few things in this world run with 100% efficiency, this is the case for inverters as well. What it means for an inverter is how much of the DC power it turns into AC power. High-quality inverters generally range from 85-95%, if an inverter is 90% efficient it means 10% of the energy is lost within the inverter, usually in the form of heat.
It is important to take this into account when figuring out how long your power supply will last as your inverter will make up for this ineffienccy y drawing more from your battery.
For example, if the 12v 800w Victron Phoenix Inverter runs at 90% efficiency. If we are running a 700w microwave it will pull around 770w from your batteries.
Hopefully this has helped you make sense of the terminology you will see when looking at inverters which will help you make an informed purchase, We have other articles that you may also be interested in such as how to pick the right size of inverter.
Have a browse through our inverter category, we have a wide range of the best inverters for boats and vans.





















